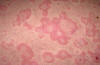
Hives ( urticaria )
Urticaria is the medical term for hives.
Hives are welts; pink/swelling they can come up on any part of the skin. They itch and each individual hive lasts a few hours before fading away, leaving no trace. New hives appear as old ones fade. They can be any size from very small or join to cover broad areas of the body. The itch can be intense. In some people the hives burn or sting.
Angioedema is similar to hives, but the swelling occurs beneath the skin instead of on the surface. It generally lasts longer than hives, but the swelling usually goes away in less than 24 hours.
There are several different types of hives
- Acute: Hives lasting less than six weeks. The most common causes are certain foods, medicines, infections, insect bites and certain diseases.
- Chronic: Hives lasting more than six weeks. The cause of this type of hives is usually more difficult to identify than those causing acute hives. For most people with chronic hives, the cause is unknown. Chronic hives can be controlled well in most people. Most all cases of chronic hives resolve with in five years.
- Physical Hives: Hives caused by direct
physical stimulation of the skin -- for example, cold, heat, sun
exposure, vibration, pressure, sweating, and exercise. The hives usually
occur right where the skin was stimulated and rarely appear elsewhere.
- Dermatographism: Hives that form after firmly stroking or scratching the skin. These hives can also occur along with other forms of hives.